How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a question many aspiring pilots ask. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, from understanding drone regulations and components to mastering advanced flight techniques and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll explore the essential steps involved in safely launching, controlling, and landing your drone, as well as best practices for responsible operation and maintenance.
Whether you’re a beginner or looking to refine your skills, this guide offers valuable insights and practical advice to help you navigate the exciting world of drone piloting.
We will cover everything from pre-flight checks and understanding airspace restrictions to advanced maneuvers like waypoints and 360-degree shots. Learn how to handle emergencies, maintain your drone, and even enhance your aerial photography and videography skills. By the end, you’ll possess the knowledge and confidence to operate your drone responsibly and enjoy the incredible possibilities it offers.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to various regulations and safety protocols. Failure to do so can result in fines, legal action, and potential harm. This section covers essential aspects of safe and legal drone operation.
Drone Licensing and Certification Requirements
Drone regulations vary depending on the type of operation (recreational or commercial) and the drone’s weight and capabilities. Recreational drone users often only need to register their drone with the relevant aviation authority (like the FAA in the US), while commercial operators require more extensive licensing and certifications. These typically involve passing knowledge tests and demonstrating safe operating procedures.
Specific requirements vary by country and region.
Airspace Restrictions and Regulations
Drone flights are subject to airspace restrictions, prohibiting operation near airports, restricted areas (military bases, prisons), and densely populated areas without proper authorization. Knowing and respecting these restrictions is paramount for safe and legal drone operation. Many countries utilize airspace maps that clearly delineate restricted areas.
Pre-Flight Safety Check Procedure

- Inspect the drone for any physical damage or loose components.
- Verify the battery is fully charged and securely connected.
- Check the propeller blades for damage or debris.
- Confirm the GPS signal is strong and accurate.
- Review the weather conditions and ensure they are suitable for flight.
- Test all controls and functionalities to ensure everything is working properly.
- Check the surrounding environment for any potential hazards or obstacles.
Maintaining Safe Distance from People and Obstacles
Maintaining a safe distance from people and obstacles is critical to prevent accidents and injuries. Always keep a clear distance from crowds and buildings, and avoid flying near power lines, trees, or other obstructions. Remember to prioritize the safety of others above all else.
Comparison of Commercial and Recreational Drone Regulations
| Regulation | Recreational Use | Commercial Use |
|---|---|---|
| Licensing/Certification | Often requires registration only | Requires comprehensive licensing and certifications |
| Airspace Restrictions | Subject to general airspace restrictions | Subject to more stringent airspace restrictions and require specific authorizations |
| Operational Limits | Typically limited to visual line of sight (VLOS) | May include beyond visual line of sight (BVLOS) operations with proper authorization |
| Insurance | Generally not required | Usually required |
Understanding Drone Components and Controls
Understanding the components of a drone and how to control them is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section details the key elements and functionalities.
Key Drone Components and Their Functions
A typical drone consists of several key components, including: the frame (provides structural support), motors (propel the drone), propellers (generate thrust), flight controller (manages flight stability and responsiveness), electronic speed controllers (ESCs) (regulate motor speed), GPS module (provides location information), battery (powers the drone), and camera (captures images and videos).
Types of Drone Controllers and Their Functionalities
Drone controllers vary in features and complexity. Basic controllers offer simple controls for takeoff, landing, and basic directional movement. More advanced controllers allow for precise control over camera functions, flight modes, and advanced maneuvers. Some controllers integrate features such as obstacle avoidance and GPS waypoint navigation.
Calibrating Drone Sensors and Gyroscopes
Calibrating the drone’s sensors (such as the accelerometer, gyroscope, and magnetometer) ensures accurate flight performance and stability. The calibration process typically involves following the manufacturer’s instructions, which often involve specific movements or positioning of the drone.
Connecting a Drone to a Mobile Device or Computer
Most modern drones connect to a mobile device or computer via Wi-Fi or other wireless protocols. This connection enables real-time control, access to camera settings, and the viewing of live video feeds. The specific connection process varies depending on the drone model and the associated app or software.
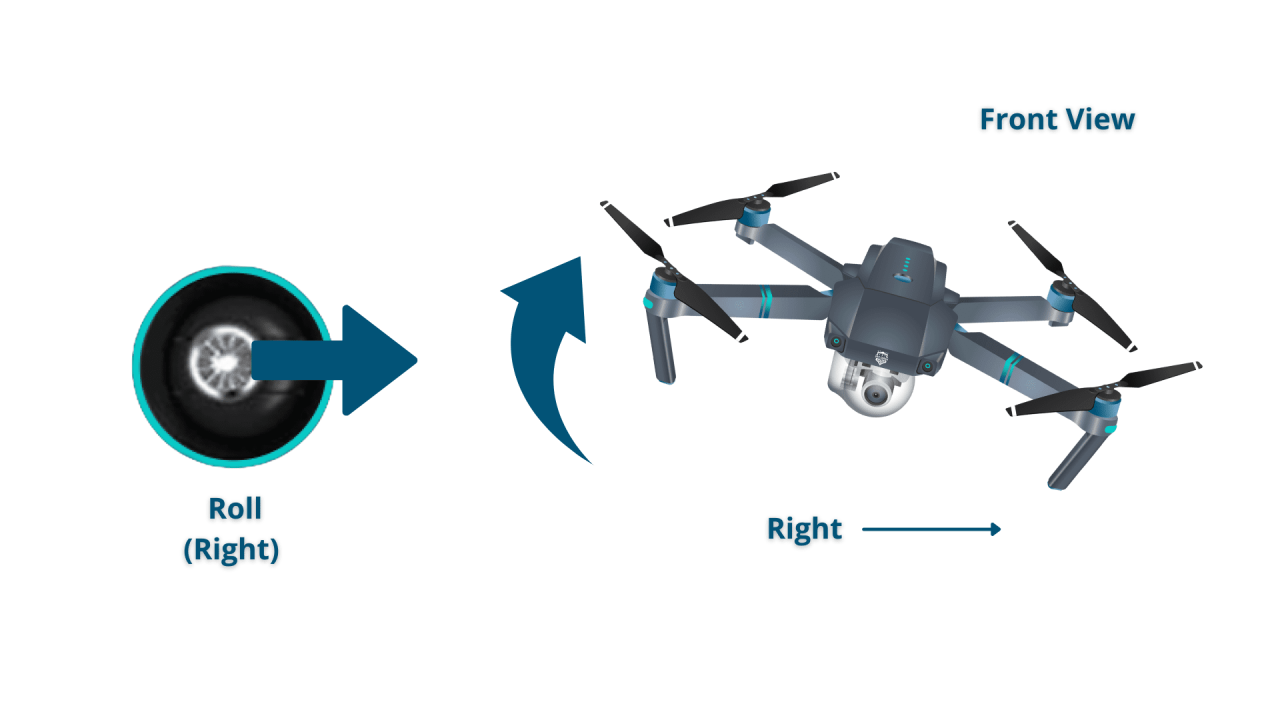
Diagram Illustrating Control Stick Inputs and Their Effects on Drone Movement

A typical drone controller uses two joysticks. The left joystick controls altitude and direction (forward, backward, left, right), while the right joystick controls the drone’s yaw (rotation) and camera tilt. A clear understanding of these inputs is essential for precise control. (Imagine a diagram here showing the left joystick controlling vertical and horizontal movement and the right joystick controlling yaw and camera tilt.)
Basic Drone Flight Procedures
This section Artikels the fundamental steps involved in operating a drone, from powering up to safe landing procedures. Mastering these basics is crucial for safe and efficient drone operation.
Powering On and Initializing a Drone
The process generally begins with turning on the drone’s battery and then the controller. The drone will then initialize its systems, including GPS acquisition, sensor calibration, and motor checks. The specific sequence varies depending on the drone model. Always consult your drone’s manual for detailed instructions.
Taking Off, Hovering, and Landing a Drone Safely
Takeoff involves gently raising the drone using the controller’s throttle stick. Hovering requires maintaining a stable position in the air, adjusting the control sticks to compensate for wind or other external factors. Landing involves gradually lowering the drone until it gently touches down. Smooth and controlled movements are essential for safe landings.
Maneuvering a Drone in Different Directions and Altitudes
Precise maneuvering is achieved by using the control sticks to adjust the drone’s pitch (forward/backward), roll (left/right), and yaw (rotation). Practice is key to developing the skills for precise and controlled movements.
Controlling Drone Speed and Responsiveness
Most drones offer different flight modes that adjust speed and responsiveness. Beginner modes typically offer slower speeds and more stable control, while more advanced modes allow for faster speeds and more agile maneuvers. Selecting the appropriate mode is crucial for safe and effective operation.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and enjoyable drone operation.
Emergency Procedures: Low Battery Handling and Unexpected Malfunctions
- Low Battery: Most drones provide low-battery warnings. Immediately initiate a safe landing procedure upon receiving such warnings.
- Unexpected Malfunctions: If the drone experiences unexpected malfunctions, attempt to regain control using basic maneuvers. If control cannot be regained, initiate an emergency landing procedure. In some cases, it may be necessary to use the Return-to-Home (RTH) function.
Advanced Drone Flight Techniques: How To Operate A Drone
Beyond basic flight, advanced techniques enhance the capabilities and possibilities of drone operation, enabling more complex maneuvers and autonomous flights.
Programming Waypoints for Autonomous Flights
Waypoints are pre-programmed points in space that the drone can autonomously navigate to. Many drone software applications allow users to define waypoints on a map, creating complex flight paths for automated aerial photography or inspections. This requires careful planning and consideration of airspace restrictions.
Using Return-to-Home (RTH) Functionality
The RTH function enables the drone to automatically return to its home point (takeoff location) if it loses signal or the battery gets low. This is a crucial safety feature that helps prevent loss or damage to the drone.
Achieving Smooth and Stable Drone Shots During Video Recording
Smooth and stable shots require precise control and potentially the use of a gimbal. Using appropriate flight modes, minimizing sudden movements, and understanding wind conditions are crucial for capturing high-quality video footage.
Flying a Drone in Windy Conditions
Wind significantly impacts drone stability and control. Flying in windy conditions requires careful planning, adjusting flight parameters to compensate for wind gusts, and understanding the drone’s wind resistance capabilities. It is often advisable to avoid flying in extremely windy conditions.
Performing a 360-Degree Aerial Shot
A 360-degree aerial shot involves slowly rotating the drone while capturing video or a series of images. This requires smooth and precise control, potentially using a gimbal to stabilize the camera and ensure smooth transitions. Appropriate camera settings are also important to capture consistent exposure and focus.
Drone Photography and Videography
This section covers essential techniques and considerations for capturing high-quality aerial photography and videography using a drone.
Composing Compelling Aerial Shots and Videos
Good aerial shots involve careful consideration of composition, including the rule of thirds, leading lines, and the use of foreground and background elements to create visual interest. Understanding perspective and using different angles can significantly enhance the visual appeal of aerial photography and videography.
Adjusting Drone Camera Settings for Different Lighting Conditions
Proper camera settings are crucial for capturing well-exposed images and videos in various lighting conditions. Adjusting aperture, shutter speed, and ISO to compensate for changes in light levels is essential for optimal results. Understanding the relationship between these settings is vital for achieving the desired look and feel.
Transferring Drone Footage to a Computer for Editing
Drone footage is typically transferred to a computer using a memory card reader or by wirelessly transferring files via Wi-Fi. The specific method depends on the drone model and the associated software. Once transferred, the footage can be edited using video editing software.
Essential Accessories for Enhancing Drone Photography and Videography
- Neutral Density (ND) Filters: Reduce the amount of light entering the camera, allowing for slower shutter speeds and wider apertures.
- Gimbal: Stabilizes the camera, resulting in smoother video footage.
- Polarizing Filters: Reduce glare and reflections, enhancing color saturation and clarity.
Visual Characteristics of Good Aerial Cinematography, How to operate a drone
Good aerial cinematography is characterized by smooth camera movements, well-composed shots, and a clear narrative or visual story. Using a variety of shots, angles, and transitions can enhance the visual appeal and storytelling potential of the footage.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its reliable operation. This section provides guidance on these essential aspects.
Schedule for Regular Drone Maintenance Tasks
Regular maintenance should include cleaning the drone body and propellers, inspecting for damage, checking the battery health, and lubricating moving parts as needed. A detailed maintenance schedule should be developed based on the frequency of use and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Their Possible Causes
Common malfunctions include motor issues, GPS signal loss, battery problems, and camera malfunctions. Identifying the cause of a malfunction often requires careful observation and investigation, sometimes involving troubleshooting steps Artikeld in the drone’s manual.
Troubleshooting Steps for Resolving Typical Drone Problems
Troubleshooting steps often involve checking connections, inspecting components for damage, recalibrating sensors, and updating firmware. A systematic approach to troubleshooting is essential for efficient problem resolution.
Checklist for Inspecting a Drone Before and After Each Flight
- Inspect the drone body for damage.
- Check the propellers for damage or debris.
- Verify the battery level and condition.
- Test the motors and controls.
- Check the camera and gimbal.
Tips for Extending the Lifespan of a Drone Battery
Proper battery care is essential for extending its lifespan. This includes avoiding extreme temperatures, storing the battery at a moderate charge level, and avoiding overcharging or discharging.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a journey of continuous learning and practice. From understanding the intricate details of drone regulations and mechanics to mastering advanced flight techniques and capturing breathtaking aerial imagery, this guide has equipped you with the foundational knowledge to embark on this exciting adventure. Remember, responsible drone operation is paramount, so always prioritize safety and adhere to all applicable regulations.
With dedication and practice, you’ll soon be soaring through the skies, capturing stunning visuals, and exploring the boundless possibilities of aerial technology.
Detailed FAQs
What type of battery is best for my drone?
The best battery type depends on your drone model. Check your drone’s manual for recommended battery specifications. Generally, lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries are common.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s sensors?
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to navigating different flight modes. Mastering these skills ensures safe and enjoyable drone operation.
Calibrating your drone’s sensors is important before each flight session, especially after a crash or significant impact. Consult your drone’s manual for specific calibration instructions.
What should I do if my drone loses signal?
Most drones have a Return-to-Home (RTH) function. If the signal is lost, the drone will attempt to return to its takeoff point. However, always keep your drone within visual line of sight to avoid accidents.
How do I clean my drone propellers?
Gently clean your propellers with a soft brush or cloth after each flight to remove dirt and debris. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials.
